🤖 Summarize this article with AI:
💬 ChatGPT 🔍 Perplexity 💥 Claude 🐦 Grok 🔮 Google AI Mode
End-to-end testing is essential for modern software teams. If you’ve ever wondered what is end-to-end testing or why it matters, the answer is simple: it ensures your entire application works the way users expect.
Validating the application from the end user's perspective is crucial to ensure real-world usability and reliability. Instead of testing single features in isolation, end-to-end testing tools validate complete user journeys—like signing up, searching, checking out, or connecting with third-party services—ensuring that workflows function correctly from the user's perspective.
Insufficient or delayed testing can negatively affect users by allowing issues to reach production and impact user experience, revenue, and trust.
In this guide, we’ll explain what end-to-end testing means in software testing, why it’s important, and how to implement it with the best frameworks and practices available today.
🎯 TL;DR - E2E Testing
-
E2E testing validates real user journeys across the full stack, ensuring workflows like signup, search, checkout, and third-party integrations behave correctly—catching issues that unit or integration tests may miss.
-
Benefits span UX, reliability, and risk mitigation: verify end-user experience, data integrity, subsystem interactions, and stability; get immediate, user-like feedback on failures.
-
Implementation hinges on disciplined planning: define user functions and cross-system flows, set measurable conditions, create realistic test cases (multi-browser/device), maintain tests continuously, and integrate E2E early in the dev cycle.
-
Tooling matters: frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, TestCafe, Appium and platforms like LambdaTest/New Relic/Headspin/Endtest serve different needs; choose based on scale, ecosystem, and CI/CD fit.
-
BugBug accelerates low-code E2E with a fast recorder, Edit & Rewind debugging, built-in email testing, zero extra infra, and smooth CI/CD/Slack integrations—letting teams ship confidently with less maintenance.
Check also:
- 🎯 TL;DR - E2E Testing
- What Is End-to-End Testing?
- Why is End-to-End Testing Important?
- What Are The Benefits of End-to-end Testing?
- How to Implement End-to-End Testing?
- What Are End-to-End Test Cases For Your Testing Process?
- Best End-to-End Testing Tools
- End-to-End Testing Frameworks
- Summary: End-to-End Testing Explained
- Frequently Asked Questions about E2E Testing
What Is End-to-End Testing?

End-to-end testing is a key testing strategy within software development that examines the functionality and performance of an application in conditions that mimic real-world usage. It ensures that all the integrated components of an application interact perfectly and accomplish expected tasks without issues.
End-to-end testing evaluates the complete system, validating all integrated components to simulate real user scenarios. E2E testing validates the entire user journey, ensuring all steps from start to finish work as intended.
This type of testing spans the entire software product—from the front end to the back end, and all the touchpoints in between, encompassing various aspects of software testing such as UI, API, and regression testing. E2E testing is especially important in environments where applications interact with multiple systems and databases.
System testing is typically performed before end-to-end testing, focusing on validating the application’s core functions and integration points within the overall testing hierarchy.
Key Features:
- UI Tests for Desktop and Mobile: E2E testing involves creating test scenarios for user interfaces on both desktop and mobile platforms to ensure applications are responsive and user-friendly, validating the entire workflow from start to finish and helping verify the software’s functionality from the user’s perspective.
- API Testing: It validates that APIs meet functionality, reliability, performance, and security expectations.
- Cross-Browser Testing: This ensures that the application functions correctly across different web browsers, enhancing the user experience.
- Regression Testing: E2E tests are crucial for verifying that recent code changes have not adversely affected existing functionalities.
Why is End-to-End Testing Important?
Is End-to-End testing necessary? It is true that more and more developers make sure to implement an E2E testing phase before the final deployment of their software. Development teams play a crucial role in structuring and executing E2E tests, ensuring software quality and user satisfaction. There are many benefits to E2E tests, but the most crucial ones are:
- The ability to verify software performance from the end-user perspective
- Testing verifies not only the software itself but also any interrelated sub systems, increasing test coverage
- Validation of back-end systems, and verification of data integrity across interconnected systems
- Immediate end-user-like feedback on test failing
- Improvement of overall software quality by ensuring all components work together as expected
- Enhanced system stability by identifying and addressing issues that could compromise the application's reliability
Integration testing verifies the correct interaction between individual software modules, complementing E2E testing by ensuring that each part works together seamlessly.
💡 If you’re new to software automation, take a look at this beginner’s guide to automation with step-by-step screenshots.
What Are The Benefits of End-to-end Testing?
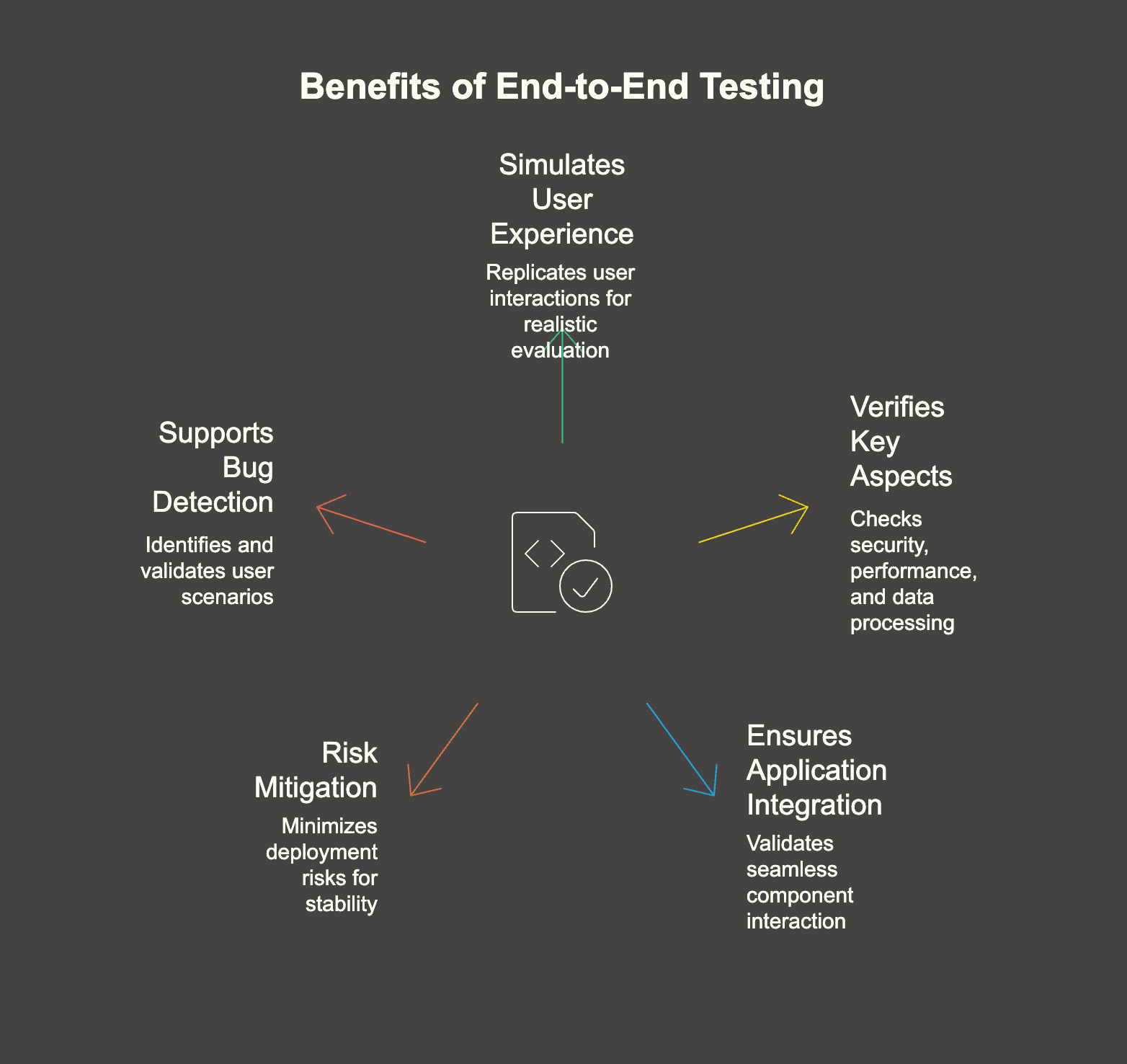
- Simulates the End-User Experience: E2E testing replicates how a user interacts with the software, providing a realistic evaluation of its performance and behavior. Usability testing is a key component of E2E testing, as it evaluates the user experience and helps identify usability issues by observing real user interactions. This comprehensive approach enhances user satisfaction by ensuring the application performs well in real-world scenarios.
- Verifies Key Aspects: It checks not only security and performance but also ensures that the software accurately collects and processes data as intended, covering the business logic thoroughly. The use of accurate test data is essential to ensure realistic validation during these checks.
- Ensures Application Integration: E2E testing validates that all integrated components of the application work seamlessly together, ensuring a consistent and reliable user experience.
- Risk Mitigation: By verifying the software’s readiness for deployment, E2E testing minimizes risks, providing stability and reliability—key factors for stakeholder approval.
- Supports Bug Detection and Scenario Testing: E2E testing identifies bugs and validates different user scenarios, ensuring comprehensive coverage and quality assurance. Additionally, it can simulate user interactions by automatically executing test cases across different systems, which is crucial for maintaining efficiency and accuracy. E2E testing ensures that all critical paths are properly tested before deployment.
Start e2e tests in 5 minutes
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
How to Implement End-to-End Testing?
Alright, so now you know what End-to-End testing is – but how to exactly implement it? There is a wide variety of checks and individual tests that must be covered by your end-to-end test planning, some of which include:
- Establishing test requirements in the preparation phase (including software and hardware requirements)
- Creating proper documentation
- Deciding what type of test environment will be used (production environment or independent test environment) – It is important to set up appropriate test environments tailored to different testing focuses, such as integration and end-to-end tests, to ensure accurate and reliable results.
- Preparation of test cases and general E2E design – This includes the challenges involved in designing tests that accurately simulate real-world user interactions across different browsers and specifications.
- Tracking of data input and output
- Test execution and evaluation
Integrating E2E testing early in the development process is crucial to ensure effective communication among components and enhance overall project success. Ongoing test maintenance is also necessary to keep automated test scripts up to date as the application evolves. When selecting testing tools and planning for long-term test upkeep, it is important to consider maintenance costs to ensure strategic decision-making and maximize ROI.
Establish User Functions
The User Functions relates to listing the features of your software, as well as all of its interconnected software systems. To properly measure and test software functionality, you need to first think about what you’re going to test.
Understanding critical business processes is essential, as disruptions to these processes can directly affect outcomes like customer satisfaction and revenue. Establishing user functions often requires collaboration within a cross team group, including developers, testers, managers, and business owners, to ensure all perspectives are considered. After you’re finished with listing user functions, remember to record everything relevant to each of them, including both the input and output data.
Since E2E testing can be considered holistic, you also need to pay attention to all of the relations between every individual function – how they work together and whether there are any clashes. Additionally, it is important to map out user interaction flows to ensure all possible user actions are covered during testing.
Come up with specific conditions
Now that you have established the user functions you’re going to test, you need to think about the testing conditions. Try to come up with as many quantifiable indicators that can be measured for each of the functions. These can range from response time to consistency of data flow, to simple convenience of use. Remember – you’re trying to imagine yourself as an end-user, so try to keep track of anything that might be an issue for a non-developer.
Create individual test cases
Finally, before E2E testing can commence, you need to prepare specific test cases for each condition. Each e2e test should simulate a complete user scenario from start to finish, ensuring the entire application is verified under real-world conditions.
End-to-end (E2E) test cases are essential for validating complete workflows by simulating the end user’s behavior.
Unlike unit tests, such tests provide broader coverage by running in a realistic test environment that ensures test environment availability and allows the use of realistic data or sanitized production data for testing purposes.
Since applications run on multiple devices, E2E testing includes multiple test cases across browsers and platforms. This approach is more reliable than relying on a single separate test case, as it helps detect issues that may only appear under specific conditions.
E2E test cases are also more detailed test cases, capturing full user journeys such as login, checkout, or payments. While these tests can be time-consuming, consistent test runs provide higher confidence in software quality. Ultimately, E2E testing prevents costly production issues and ensures smoother, real-world user experiences.
What Are End-to-End Test Cases For Your Testing Process?
Typical end-to-end test cases cover the most critical user flows in a web or SaaS application.
- User Authentication & Access – Sign up with valid credentials, sign up with invalid or duplicate credentials, login with correct or incorrect credentials, password reset flow (request, email link, reset, login), multi-factor authentication, and session timeout with re-login.
- User Profile & Account Management – Update profile information such as name, email, or password; change email and verify confirmation link; and delete or deactivate the account.
- Navigation & Core Workflows – Navigate between key pages using menus, links, and the browser back button; validate breadcrumb trails and redirects; and test mobile or responsive navigation across devices.
- Form Handling – Submit forms with valid data, attempt submission with invalid or missing data to check error messages, test draft saving or auto-save functionality, and upload files with both supported and unsupported formats.
- Search & Filtering – Perform searches with exact matches, partial or invalid inputs, apply multiple filters simultaneously, and reset filters to verify results.
Best End-to-End Testing Tools
- BugBug – A no-code, cloud-based end-to-end (E2E) testing tool designed for Agile teams, enabling quick test creation, real browser execution, and CI/CD integration. BugBug allows users to easily create tests without extensive technical knowledge, making it accessible for non-technical users. Features like visual modeling and drag-and-drop interfaces enable faster test creation.
- BrowserStack – A cloud-based testing platform that lets teams run manual and automated tests across 3500+ real browsers, devices, and operating systems. It supports frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, Appium, and Playwright, and uses smart AI agents in every step of the testing life cycle to optimize, self-heal and speed up tests. With real-device testing, parallel execution, and CI/CD integration, teams achieve faster, more reliable releases at scale.
- LambdaTest – An AI-powered test execution platform that runs manual and automated tests at scale across browsers, devices, and operating systems. LambdaTest supports parallel testing, allowing multiple tests to be executed simultaneously to speed up test execution. It also offers features for faster test creation, such as pre-built templates and intuitive interfaces.
- New Relic – A full-stack observability platform that delivers real-time performance monitoring, analytics, and customizable dashboards for applications and infrastructure.
- Endtest – An automated testing tool with cross-browser support, video recordings, and automated result analysis to simplify debugging and quality assurance. Endtest can automate most tests, providing high coverage and efficiency for comprehensive test automation.
- Headspin – A global testing platform providing real-device and real-network condition testing with AI-driven performance insights and secure, scalable operations.
BugBug - The Best E2E Testing Tool for Web Applications
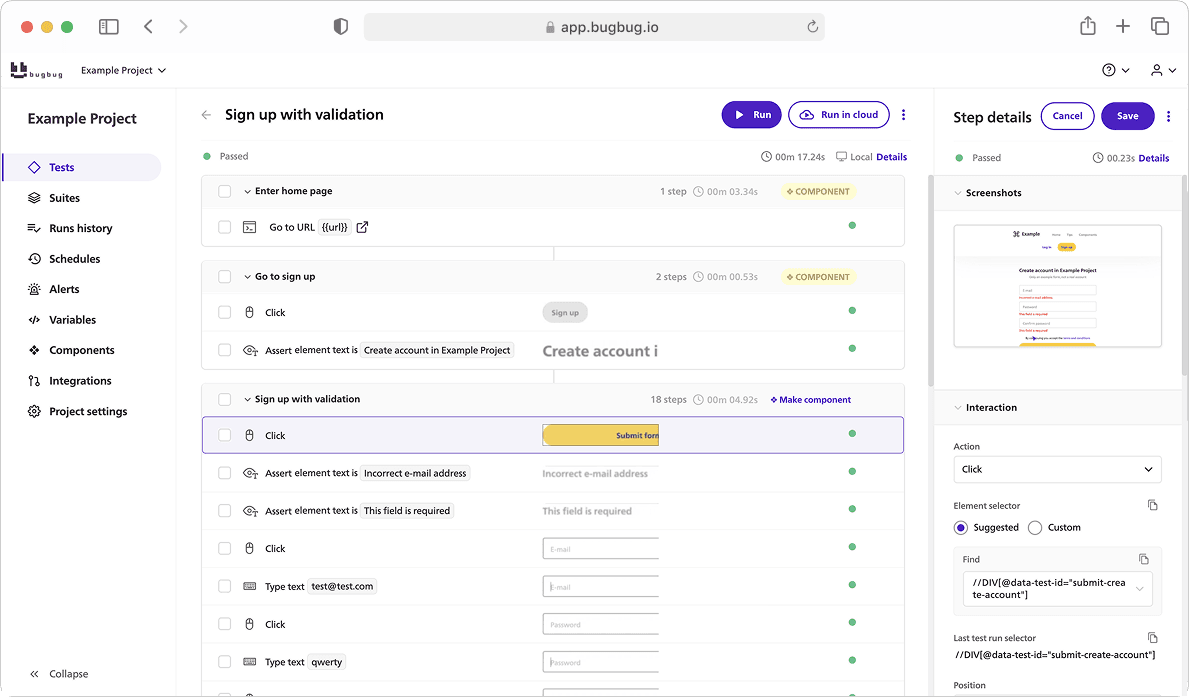
BugBug is a user-friendly, cloud-based automated testing tool designed specifically for agile teams. It enables rapid and easy creation of end-to-end test scenarios through a no-code interface, making it ideal for frequent iteration and deployment cycles.
Key Features:
👾 Super simple, yet powerful
BugBug combines an intuitive interface with advanced capabilities. The UI/UX is designed for speed and clarity.
👾 Run tests locally or in the cloud
With BugBug, you can run tests on your own machine for quick checks or schedule them in the cloud for continuous monitoring. No extra setup or infrastructure is required.
👾 Edit & Rewind
BugBug lets you insert new steps anywhere in a test and resume execution from any point. This makes debugging, refining, and maintaining tests much easier compared to traditional frameworks.
👾 Built-in email testing
Thanks to bugbug-inbox.com, you can test email flows directly in your end-to-end scenarios. Perfect for verifying signup confirmations, password resets, or transactional emails without leaving the platform.
👾 No extra infrastructure
Unlike Selenium grids or heavy testing platforms, BugBug doesn’t require additional servers, Docker setups, or virtual machines. It’s lightweight and ready to use out of the box.
👾 Custom JavaScript actions
For advanced needs, BugBug supports custom JavaScript steps. This makes it possible to cover edge cases and complex user interactions that other no-code tools can’t handle.
👾 Seamless integrations
BugBug connects easily with CI/CD pipelines, Slack, and other tools your team already uses, fitting smoothly into modern development workflows.
How to Run End-to-End Tests with BugBug?
💡 Check out the video and start testing!
Anyone on a SaaS team—PMs, developers, or testers—can use BugBug to run end-to-end (E2E) tests that replicate real-world user scenarios.
BugBug enables you to run tests that cover the entire user journey from the user's perspective, ensuring your application works as intended in real-world conditions. Define your test scope, record UI tests in minutes, and start catching bugs before your users do.
Start low-code testing with BugBug
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
LambdaTest

LambdaTest is an AI-powered test execution platform that enables developers and testers to run their manual and automated end-to-end tests at scale. It supports various testing tools and frameworks for web and mobile app testing, ensuring exceptional user experience across various browsers, devices, and operating systems. With LambdaTest, teams can run e2e tests in parallel and reduce test execution times, helping them provide faster feedback and release software applications with confidence.
Key Features:
- HyperExecute: Provides an end-to-end test orchestration platform that is faster up to 70% than conventional cloud grids.
- AI-Powered Test Analytics: Offers to assess high-impacting issues with detailed test analytics and observability suite.
- Accessibility Testing: Lets you test accessibility to ensure digital inclusivity.
Use Cases:
- Browser and App Testing: Validate the compatibility of your web and mobile applications across multiple browsers, devices, and OSes to ensure consistent user experiences.
- Automated Testing: Integrate with test automation frameworks like Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, and Appium to automate test execution and speed up the release cycle.
👉 Check out LambdaTest vs BugBug
BrowserStack

BrowserStack is a cloud-based test automation platform that empowers teams to run manual and automated end-to-end tests across real browsers, devices, and operating systems. It supports popular testing frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, Appium, and Playwright etc., enabling teams to validate web and mobile applications under real-world conditions.
With AI agents, BrowserStack intelligently generates, optimizes, and self-heals tests across the test lifecycle. With real-device cloud testing, parallel execution, and CI/CD integration, BrowserStack helps teams accelerate release cycles, enhance test reliability, and deliver flawless digital experiences at scale.
Key Features:
- Test Management: Create, manage, and track manual and automated test cases with integrated workflows and real-time dashboards.
- AI-powered Reporting: Automated test reporting, debugging and analysis using AI to categorise failures, tracks suite health and metrics, and enables real-time insights for UI, API and unit tests.
- Integration with Development Tools: Seamlessly integrates with tools like JIRA, GitHub, test automation frameworks and CI/CD pipelines to streamline workflows.
Use Cases:
- Cross-Browser and Real Device Testing: Instantly test websites and mobile apps across thousands of real browsers, operating systems, and 20,000+ iOS and Android devices.
- Accessibility Testing: Automate accessibility checks for websites and mobile apps to ensure compliance with WCAG, ADA, and other global standards powered AI-driven Spectra™.
New Relic
New Relic is a comprehensive observability platform that offers deep insights into the performance of applications, networks, and infrastructure. Its powerful analytics capabilities and customizable dashboards make it essential for real-time monitoring and optimization in dynamic environments.
Key Features:
- Full-Stack Observability: Provides insights into applications, infrastructure, and network performance in one platform.
- Real-Time Analytics: Offers real-time performance metrics and operational data.
- Customizable Dashboards: Allows the creation of custom dashboards to monitor specific metrics.
Use Cases:
- Performance Monitoring: Helps businesses monitor and optimize the performance of their web applications and infrastructure.
- DevOps Teams: Enables DevOps teams to quickly identify and address performance issues to maintain service reliability.
Endtest
Endtest is an automated testing tool that provides an intuitive framework for executing and analyzing test cases across various platforms and browsers. Its focus on automated result analysis and video recording features make it a valuable asset for continuous testing and debugging.
Key Features:
- Automated Result Analysis: Provides tools to automatically analyze test case results, identify trends, and detect anomalies.
- Cross-Browser and Cross-Platform Testing: Supports testing across multiple browsers and platforms.
- Video Recordings: Captures video recordings of test sessions to assist in debugging.
Use Cases:
- Quality Assurance: Useful for QA teams to efficiently analyze test outcomes and refine testing strategies.
- Automated Software Testing: Ideal for organizations that want to implement robust automated testing frameworks with detailed result analysis.
Headspin
Headspin provides a global platform for testing mobile and web applications on real devices under actual network conditions. Its AI-driven analytics and robust security features support scalable and efficient testing operations, ensuring high performance across diverse user environments.
Key Features:
- AI-Powered Performance Insights: Offers detailed, AI-driven insights into application performance and user experience.
- Device Cloud: Provides access to a global device cloud for testing applications on real devices under different network conditions.
- Secure Testing Operations: Ensures high levels of security for testing data and operations.
Use Cases:
- Global App Testing: Suitable for businesses needing to test applications under various real-world conditions globally.
- Scalable Testing Operations: Helps organizations that need to scale their testing operations securely and efficiently, particularly useful for mobile applications.
Each of these tools offers unique features tailored to specific testing needs, supporting teams in maintaining high-quality software delivery processes.
End-to-End Testing Frameworks
End-to-end testing frameworks are essential tools designed to simulate real user scenarios to validate the complete functionality of an application, from the front end to the back end, including its integration with other systems.
End-to-end testing is critical for verifying the overall system’s health, highlighting issues that unit or integration tests might miss. Such frameworks often support automation to streamline the testing process, enhance accuracy, and reduce the time and resources needed for manual testing.
👉 Check also our Ultimate Guide to Test Automation Frameworks
Selenium

Selenium is the industry standard for automating web browsers. It provides a set of tools and libraries that enable web browser automation. It's particularly known for its Selenium WebDriver, which allows you to create robust, browser-based regression automation suites and tests.
- Key Features:
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Test scripts can run across different browsers like Chrome, Firefox, IE, and Safari.
- Language Support: Supports various programming languages including Java, C#, Python, Ruby, and JavaScript.
- Selenium Grid: Facilitates simultaneous testing across different devices and platforms.
- Community and Integrations: Extensive community support and integration capabilities with other software.
Use Cases: Selenium is ideal for testing scalable web applications across different browsers and platforms. It is particularly suited for teams that require flexibility in programming languages and customizability in test automation scripts.
💡 Check also Selenium vs BugBug
Cypress

Cypress is a front-end automated testing application created for the modern web. Its architecture allows tests to run directly inside the browser, which simplifies debugging and speeds up test execution.
Key Features:
- Automatic Waiting: Automatically waits for commands and assertions before moving on. There’s no need to define implicit and explicit waits.
- Real-Time Reloads: Test suite automatically reloads upon test script changes.
- Developer Tools: Accessible debugging tools through familiar tools like Chrome DevTools.
- Network Traffic Control: Ability to stub network traffic and manage the behavior of network requests and responses.
Use Cases:
Cypress is best for developers and QA engineers who work on complex modern web applications using frameworks like Angular, React, or Vue.js. It excels in environments where quick test development and frequent test execution are required.
Playwright

Playwright is a node library to automate the Chromium, WebKit, and Firefox browsers with a single API. It is built to handle modern web applications including single-page apps that rely heavily on JavaScript.
Key Features:
- Cross-Browser Testing: Supports testing across Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
- Headless Testing: Supports headless testing for all browsers which is faster and uses less memory.
- Rich Set of APIs: Extensive APIs to handle modern web features such as single-page applications, web components, and more.
- Network Stubbing: Allows mocking of network requests during testing.
Use Cases: Playwright is suitable for developers and testers who need an all-encompassing tool to handle the complexities of modern web apps across multiple browsers. It is especially effective in continuous integration and deployment pipelines.
💡 Check our article on Playwright Recorder vs BugBug
Appium

Appium is an open-source tool for automating mobile applications. It supports both iOS and Android platforms, making it versatile for cross-platform testing.
Key Features:
-
Cross-Platform Testing: Write tests against multiple platforms (iOS, Android), using the same API.
-
Supports Multiple Languages: Compatible with all major programming languages and test frameworks.
-
No App Modification Required: No need to modify any app code for testing.
-
Integration with Selenium: Uses the same WebDriver protocol.
Use Cases: Appium is perfect for application developers who need to ensure their product functions correctly across the most popular mobile operating systems and devices. It is also ideal for teams utilizing a single code base across multiple platforms.
Summary: End-to-End Testing Explained
- Create a solid test plan
– Focus on test planning that reflects real user scenarios and critical user paths. - Choose the right test automation tools
– Select automation tools or end testing tools that support the entire application, including desktop testing and web platforms. - Write detailed test cases
– Ensure detailed test cases cover the user interface, backend, and third-party services. - Automate functional and security testing
– Integrate functional testing, security testing, and database testing into the E2E flow. - Focus on horizontal testing coverage
– Test across multiple components to ensure the entire system works cohesively. - Maintain test scripts regularly
– Continuously maintain tests and test scripts to adapt to app updates. - Involve testing in the development cycle
– Involve testing teams early to align tests with user expectations. - Review test results regularly
– Establish a routine to regularly review test results and update tests based on findings. - Compare end testing vs. other methods
– Understand when to use end testing vs. unit, integration, or exploratory testing for maximum ROI.
Happy (automated) testing!



